The aim of the Innovation Manager in Shipbuilding Course was to attract talent from training centres to the shipbuilding sector by upskilling participants in key enabling technologies (KETs).
Innovation Manager in Shipbuilding Course Promotional Video
Target Audience
- Final year students or graduates in science or industrial engineering, computer science, naval or telecoms with an interest in specialising in innovation and technologies for the naval sector.
Layman Report
Learning Outcomes
Interested in running this course?
If you would like to run this course or have queries please contact Vanessa Huertas, ASIME, Spain (vanessa.huertas@asime.es).
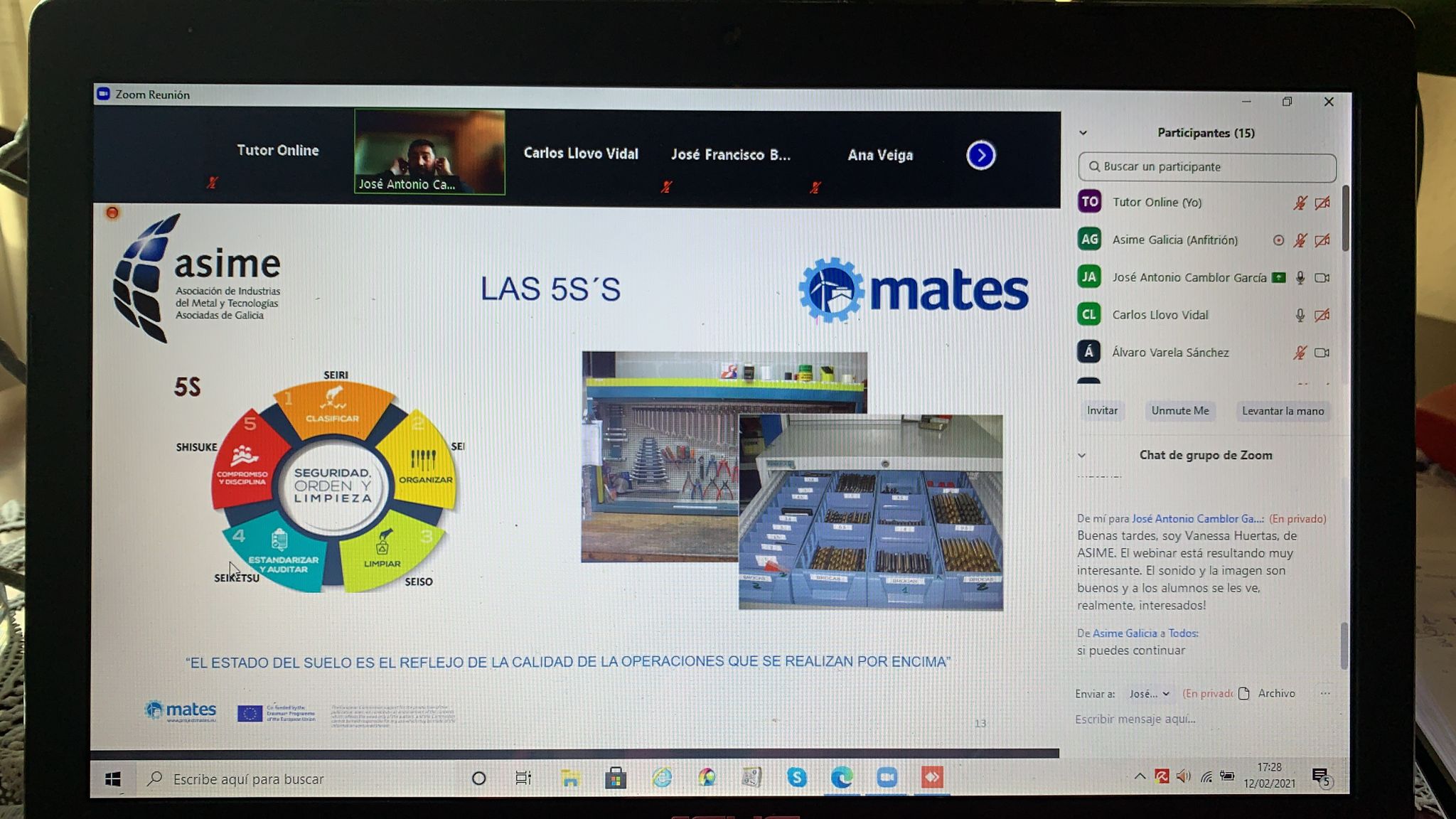
In order to attract talent to the traditional sector of shipbuilding, it is necessary to improve young peoples knowledge about it. The Innovation Manager in Shipbuilding Course was a bridging course between the end of the industrial engineering degree studies and a first job in a naval company. It introduced future workers of the sector to new methodologies and challenges by generating replicable experiences. Therefore, this Pilot Experience served as a tool for bringing new talent to the sector. Students worked in groups combined with online support materials on KETs. They were offered theoretical and practical training to acquire the necessary skills to meet the challenges that arise in this type of industry.
- Training, reskilling/upskilling workforce in the use of digital and data driven technologies (big data, Internet of Things, cloud computing, 3D printing, artificial intelligence)
- Training, reskilling/upskilling workforce in the use of automation and robotics as well as in the human –robot interactions (automation/autonomous ships, mechatronics, augmented reality)
- Progressive introduction and increasing relevance of 21st century skills within the training offer (“Soft skills” e.g. creative thinking and innovation, critical thinking and problem solving, communication and collaboration, knowledge management and transfer, flexibility and adaptability, initiative and self-direction, productivity and accountability).
- Skills ecosystems: meeting points for the most relevant stakeholders from industry, academia and research.
- Level 7
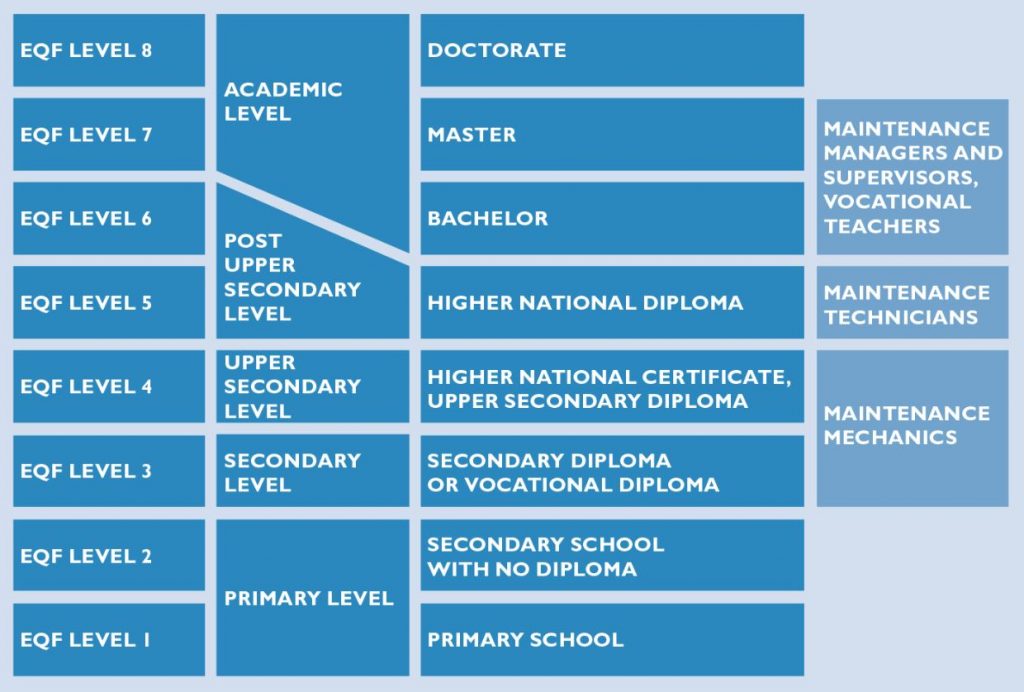
Figure 1: EQF levels compared with achieved education and maintenance personnel positions [1].
[1] Application of European Qualification Framework (EQF) in Maintenance. Magazine for maintenance & asset management professionals: maintworld.com
Time and Date
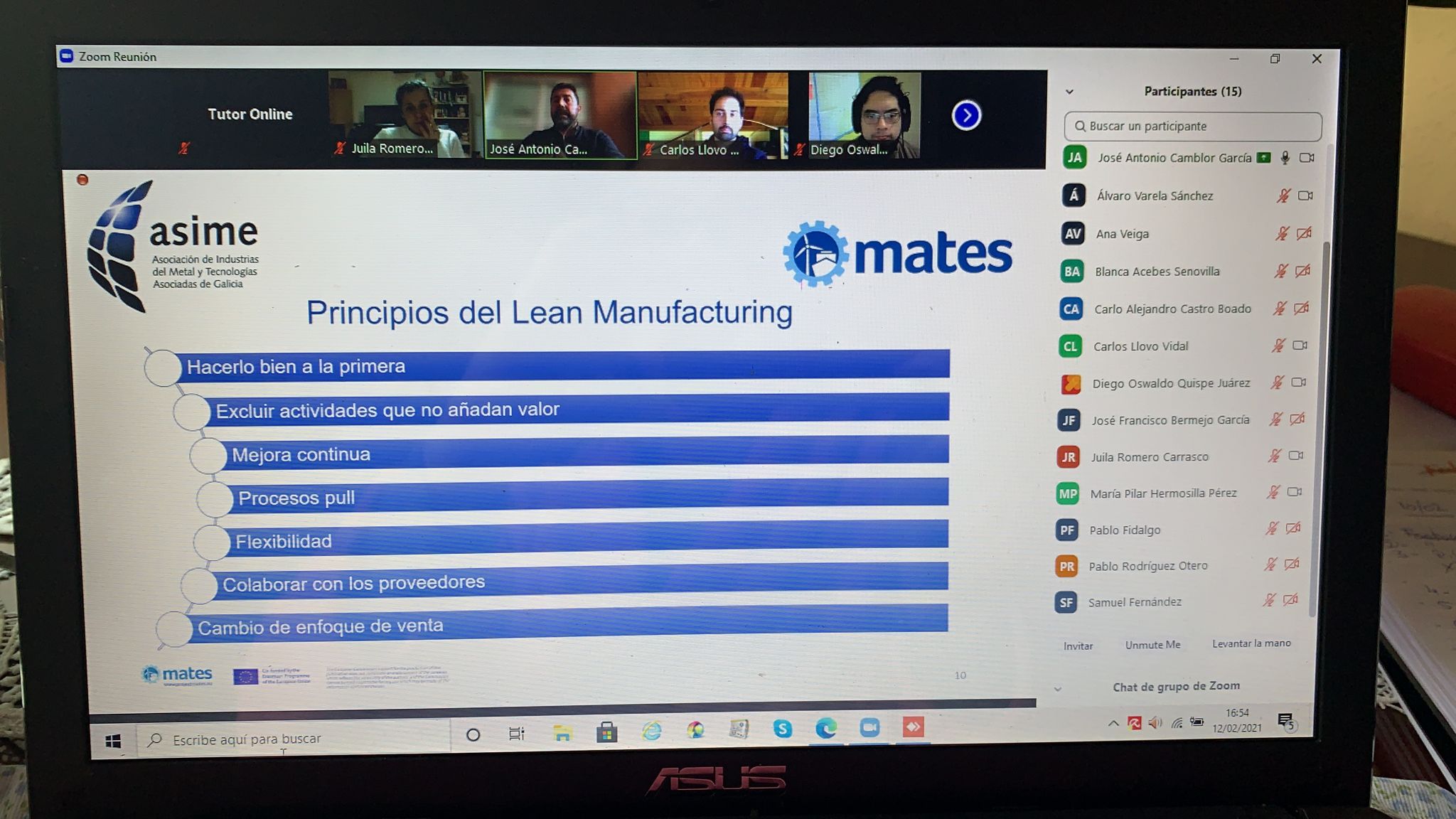
- Classes started in February 2021 and ran till 7 May 2021. The course which was predominantly online, required a dedication of two hours per day and included free online training in Lean Management and Lean Manufacturing, essential enabling technologies and project management.
- The course also involved 30 hours of mentoring with professionals from the naval and technology sector, who proposed real challenges for the students to solve, based on the day-to-day operations of the companies.
Venue
Online
Registration – NOW CLOSED
Registration for the course is free through the registration form.
Course instructors
Instructors who delivered the course belong to two main groups: shipbuilding industry workers and technologists with expertise in key enabling technologies.
The MATES Strategy Baseline report consists of results which were obtained from the extensive work carried out by the MATES partners; workshops with experts, Delphi questionnaires, desk-top studies and surveys. This report synthesises the MATES strategy baseline to bridge the skills gap between training offers and the industry demands in the Maritime Technologies value chain. The full report can be accessed here. Below are the Lines of Actions identified in the report (see pages 17 and 18) which the Innovation Manager Course addressed (SB = shipbuilding):
- SB1: Digital and data driven technologies
- SB2: Automation and robotics
- SB6: 21st century skills
- SB9: Skills ecosystems